The safe use of press brakes is crucial in maintaining workplace safety while performing metal bending and shaping operations. As a vital component in manufacturing, press brake safety cannot be overlooked by inspectors charged with the responsibility of ensuring that safety measures are in place and strictly adhered to. This article will provide comprehensive guidance for inspectors, highlighting the importance of understanding press brake operations, compliance with regulatory standards, and implementing best practices to mitigate risks and protect workers.
Understanding Press Brake Operations
Press brakes are essential tools in the metal forming industry, crucial for creating precise bends in a variety of materials. A clear understanding of their definition, applications, and types aids operators in selecting the right bending machines for their specific tasks. This section explores the fundamental facets of press brakes to foster better operational knowledge.
What is a Press Brake?
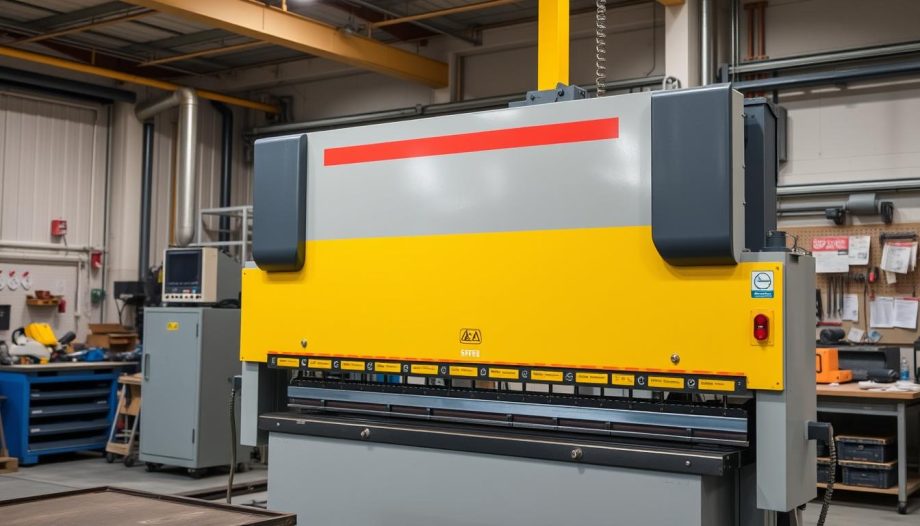
A press brake is a machine tool designed to bend sheet and plate material, a key element in the metal forming process. It consists of a stationary bed, a movable ram, and a variety of tooling options. The press brake definition encompasses machines that apply force to create bends, ensuring accuracy and repeatability in metal fabrication projects.
Common Applications of Press Brakes
The applications of press brakes extend across multiple industries, emphasizing their versatility. Common uses include:
- Manufacturing automotive components
- Creating brackets and frames in construction
- Producing enclosures and housings for equipment
- Fabrication of appliances and electronic devices
Each application highlights the importance of precision in metal forming, underscoring the need for effective operation of bending machines.
Types of Press Brakes
Understanding the types of press brakes available can greatly influence productivity and efficiency in fabrication environments. Key classifications include:
| Type of Press Brake | Description | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Press Brake | Uses a ram driven by a mechanical crank for bending | High-speed production of small to medium parts |
| Hydraulic Press Brake | Employs hydraulic cylinders for bending, offering more flexibility | Producing larger and thicker parts |
| Electric Press Brake | Utilizes electric drives for controlled and efficient operation | Applications demanding precision and energy efficiency |
Choosing the right type of press brake plays a significant role in the overall efficiency and accuracy of the metal forming tasks.

Safe Use of Press of Brakes (Guidance for Inspectors)
Inspectors play a crucial role in ensuring the safe operation of press brakes within manufacturing environments. Understanding and implementing proper press brake safety protocols is vital to prevent accidents and ensure compliance with workplace safety procedures. This section highlights the importance of rigorous safety measures, essential safety features to examine, and effective inspection best practices that contribute to a safer workplace.
Importance of Safety Protocols
Establishing robust press brake safety protocols protects operators and fosters a culture of safety within the workplace. Adhering to these protocols minimizes the risk of injuries and enhances overall productivity. Regularly reviewing and updating these safety measures ensures they meet evolving industry standards and risk assessments.
Key Safety Features to Inspect
The inspection of press brakes should include a thorough evaluation of critical safety features designed to prevent accidents. Key safety features include:
- Two-hand control systems that require both hands for operation, reducing the risk of unintended engagement.
- Light curtains or safety mats that detect obstructions and halt operations if a worker enters a dangerous zone.
- Emergency stop buttons located within easy reach for immediate shutdown in case of an emergency.
- Proper shielding to protect operators from flying debris or sudden machine movements.
Best Practices for Inspectors
Implementing inspection best practices ensures thorough and effective evaluations of press brakes. Inspectors should follow these guidelines:
- Conduct routine inspections using established checklists that include all critical safety features and operational functions.
- Document findings meticulously, noting any discrepancies or required repairs for follow-up actions.
- Engage operators in safety discussions to promote an understanding of risks and encourage reporting of potential hazards.
- Stay updated on industry regulations and advancements in safety technology to enhance inspection processes.
Following these safety guidance measures will significantly improve workplace safety and enhance the operational efficiency of press brakes. Consistent practice of these protocols and features will cultivate a safer working environment for everyone involved.
Common Hazards and Risks
Understanding the various hazards related to press brake operations is crucial for enhancing workplace safety. Identifying these risks empowers inspectors to implement effective safety risk management strategies. Continuous vigilance in hazard identification prevents potential accidents and ensures a safer working environment.
Identifying Potential Hazards
Inspectors must keenly observe the work environment for various press brake hazards. Common dangers include:
- Inadequate guarding mechanisms leading to physical contact with moving parts.
- Electrical hazards from improper wiring or malfunctioning equipment.
- Pinch points resulting from material handling and machine operation.
- Noise pollution causing hearing damage over prolonged exposure.
Mitigation Strategies for Inspectors
Effective safety risk management requires proactive strategies to mitigate identified hazards. Key approaches include:
- Implementing engineering controls, such as installing safety guards and emergency stop buttons.
- Ensuring proper training programs for operators focusing on safe operational practices.
- Promoting regular maintenance checks to ensure all safety features function effectively.
- Conducting risk assessments regularly to identify new hazards as they arise.
Reporting and Documenting Safety Issues
Establishing robust safety reporting procedures is essential for tracking hazards and ensuring accountability. Inspectors should document all findings and actions taken. This documentation should include:
| Date | Hazard Identified | Action Taken | Follow-Up Needed |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10/01/2023 | Pinch point near operator station | Guard installed | Check compliance in one month |
| 10/10/2023 | Electrical wiring inspection | Repaired faulty wiring | Routine checks quarterly |
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Understanding regulatory compliance is paramount for organizations utilizing press brakes. Adhering to press brake safety standards, particularly those established by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), ensures that operators can work within a safe environment. The stringent OSHA requirements provide guidelines that protect not only the workforce but also the organization itself from legal liabilities that may arise from workplace accidents.
Inspectors play a critical role in this framework by systematically evaluating equipment to ensure alignment with safety regulations. This includes checking for proper safety measures, equipment maintenance, and operator training. By enforcing compliance with these guidelines, inspectors foster a culture of safety and responsibility within the workplace, thereby minimizing the risk of accidents and injuries.
Failing to comply with established regulatory frameworks can result in severe consequences, including fines and increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies. Hence, organizations are encouraged to prioritize the implementation of safety standards and continuous training. This proactive approach not only enhances workplace safety but also contributes to operational efficiency and employee morale.

